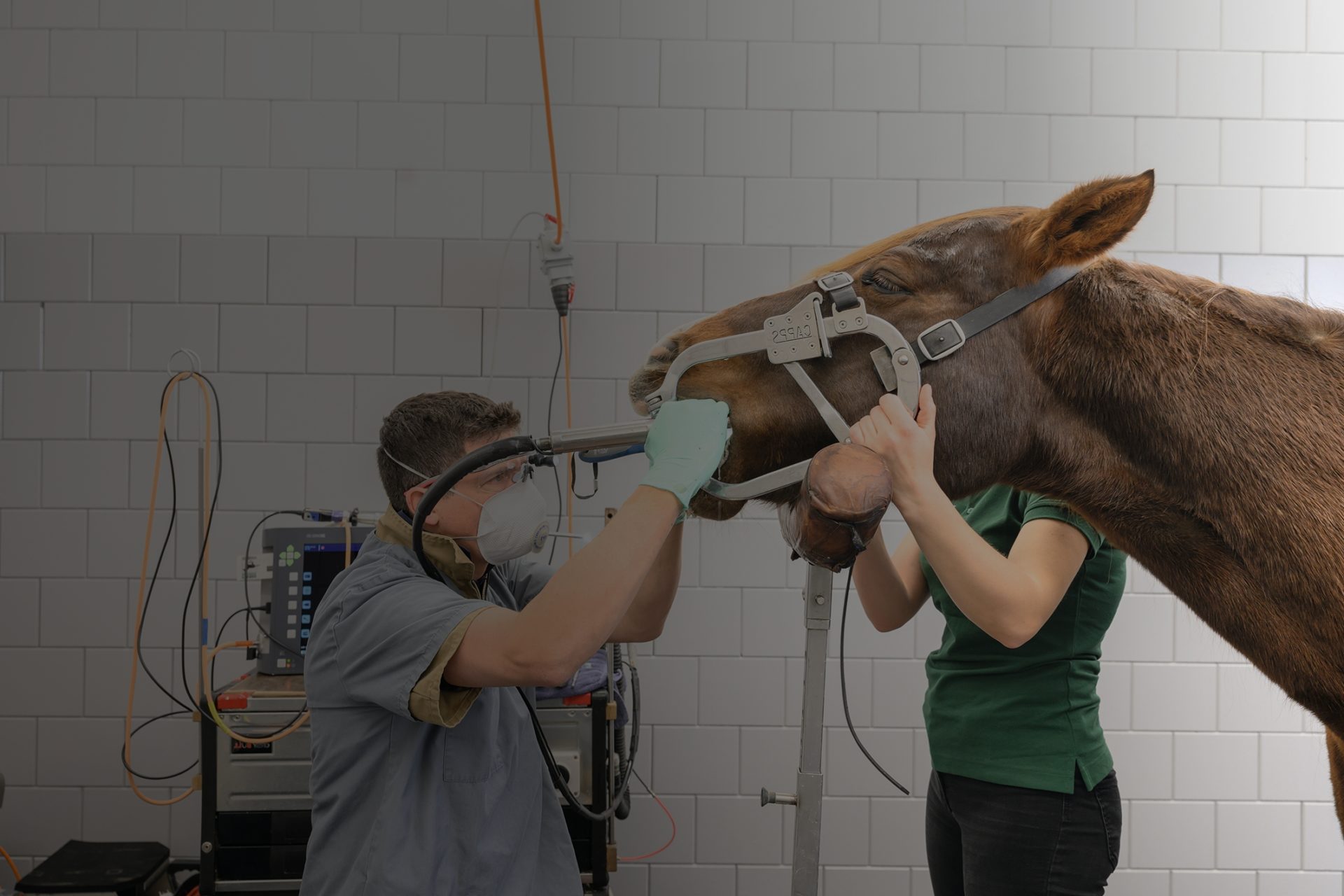
Between the ages of 2 and 5, young horses lose no fewer than 24 milk teeth, which are replaced by up to 44 permanent teeth. If they are not sufficiently abraded over time, the teeth can form into sharp points and hooks; the teeth may also break and the alveoli (dental sockets) may become inflamed. Caries, periodontitis and root infections can also pose significant problems. These issues can only be identified and properly treated through regular inspections of a horse’s oral cavity. In the case of severe diseases, X-rays and computed tomography are often needed to make a precise diagnosis.
Find specialistDentistry involves prophylactic examinations of teeth and the oral cavity as well as the diagnosis and treatment of dental diseases and associated diseases of the paranasal system.
Equine soft tissue surgery primarily relates to abdominal/colic surgery and operations in the region of the urinary system, the sexual organs, and the upper and lower respiratory tracts, as well as operations on the skin.
Dentistry involves prophylactic examinations of teeth and the oral cavity as well as the diagnosis and treatment of dental diseases and associated diseases of the paranasal system.
The specialist field of anaesthesia is concerned with professionally sedating and anaesthetising horses and sparing them unnecessary pain. Thanks to state-of-the-art methods and gentle techniques, it is now possible to perform complicated surgical procedures and life-saving emergency operations on seriously injured or sick horses and to transport them safely.
Diagnostic imaging is the process of examining a horse using digital X-ray technology, ultrasound, computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonant imaging (MRI) and scintigraphy. Nowadays, many of these diagnostic techniques do not require general anaesthesia and can be performed on a standing horse.
Dentistry involves prophylactic examinations of teeth and the oral cavity as well as the diagnosis and treatment of dental diseases and associated diseases of the paranasal system.
Diagnostic imaging is the process of examining a horse using digital X-ray technology, ultrasound, computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonant imaging (MRI) and scintigraphy. Nowadays, many of these diagnostic techniques do not require general anaesthesia and can be performed on a standing horse.